Emma Schultz, M.S. | Scientific Contributor
Updated 12/1/2023 to include latest numbers of Superfund sites by state.
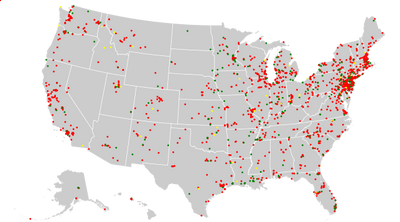
Do you know where your nearest EPA Superfund Site is? Chances are there is one close by, given that one out of every five Americans lives within three miles of an EPA-designated major hazardous waste site. There are two sites located within four miles of my childhood home, in an idyllic and quiet suburb of St. Paul, Minnesota. I now live within the same distance of five sites -- and I had no clue.
Superfund Sites - Environmental Hazards
What Is The Superfund Process?
The concept of EPA Superfund Sites is widely known and understood, but the intricacies of the program and the approach to hazardous waste mitigation are elaborate and prolonged, as can be expected of any federally-funded long-term project.
History:
In December of 1980, President Jimmy Carter signed into law the Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act (CERCLA), now known better as Superfund, which authorized the EPA to remediate hazardous waste spills and sites, and obliged those responsible for the waste - the Potential Responsible Party - to either clean it up on their own dollar or offset the cost of EPA-led cleanup efforts. Superfund had abundant funding early in its existence due to taxes levied on chemicals and oil; those taxes, however, lapsed in 1995, and financing now comes from taxpayers.
Process and Stages:
There are multiple stages in the Superfund process once a site is identified, with the first step being a Preliminary Assessment or Site Inspection. If the site is an emergency such as a chemical spill, Removal Action is taken. Otherwise, Remedial Action is planned for, which often leads to years-long planning, cleanup, and remediation. Community involvement is frequently key during the early stages of Superfund designation, and the Technical Assistance Services for Communities (TASC) program is an outreach effort designed to connect with citizens and businesses for the duration of a Superfund's existence.
After initial study, EPA Superfund Sites are given a score on the Hazard Ranking System. If a site poses enough of a threat to environmental and human health, the EPA announces its addition to the National Priorities List (NPL), pending public comment and input. NPL sites are eligible for extensive, and often long-term, federal funding through the Superfund program. These NPL-listed sites are now officially Superfund sites.
Following NPL designation, a Remedial Investigation and Feasibility Study is conducted. The Remedial Investigation collects information on-site such as water and soil samples, and the follow-up Feasibility Study analyzes various cleanup methods. The EPA then selects the most suitable cleanup alternative and provides it to the community as a Proposed Plan.
A Record of Decision notes the cleanup alternative chosen for the site. In the Remedial Design phase, the cleanup plans are drawn up, and are finally acted upon in the Remedial Action stage. A goal of Remedial Action is to return sites to productive use as quickly as possible. Whether 'productive' means industrial, housing, commercial, or greenspace depends on conversations and input from the surrounding community.
A review of EPA Superfund Site cleanup efforts occurs every five years. If cleanup goals have all been met, a portion or whole of a Superfund site may then be listed for removal from the NPL. In theory, meeting all cleanup goals sounds achievable - especially given the lengthy planning and implementation phases - but there are many sites that remain listed decades later, because groundwater and soil are still polluted.
Where Can You Learn More About Superfund Sites?
Here is the latest list of states and the number of Superfund sites they contain. Be aware that not all toxic contaminants are on the list for contaminated sites to qualify for Superfund. For example, PFAS contaminated sites are not yet regulated under CERCLA.

Resources for homeowners:
- Search for NPL Sites Where You Live - lists NPL sites near your zip code of interest
- Cleanups in My Community - shows NPL sites and more in map format
- Find Superfund Documents
- Community Involvement Tools and Resources
- To report oil or chemical spills, or other environmental emergencies, call the National Response Center at 1-800-424-8802, or visit this help page to learn more.